
ASME B16.11 Half Coupling Manufacturers and Suppliers:
A forged coupling is a type of pipe fitting that is used to connect two pipes of the same or different sizes. It is called a “forged” coupling because it is made by shaping metal through a process called forging, which involves heating the metal and then hammering or pressing it into shape.
Coupling dimensions refer to the specifications of a coupling, including its size, shape, and other physical characteristics. These dimensions are important because they determine whether a coupling will fit properly with the pipes it is intended to connect.
ISO Approved ASME B16.11 Threaded Half Coupling Manufacturer In India, ASME/ANSI B16.11 Socket Weld Full Coupling, MSS SP-79, 83, 95, 97, BS 3799 Screwed Threaded Reducing Coupling, Dimensions Chart, Tolerances, Weight Chart, Thickness Chart, Cad Drawing Forged Coupling
ADCO Forge and Fittings is a manufacturer of high-quality forged couplings and other pipe fittings, known for its expertise in forging technology and precision machining. Offers a wide range of couplings, including half couplings, full couplings, threaded couplings, and socket weld couplings, which meet various industry standards and specifications such as ASME B16.11. We are committed to providing its customers with reliable and durable products that meet specific needs and requirements.
There are two main types of forged couplings: half couplings and full couplings. A half coupling is used to connect one end of a pipe to a fitting, while a full coupling is used to connect two pipes together.
Threaded couplings are designed to be screwed onto the ends of pipes, while socket weld couplings are welded onto the ends of pipes. ASME B16.11 is a standard that specifies the dimensions and other requirements for forged fittings, including couplings. ASME B16.11 couplings are commonly used in high-pressure piping systems in industries such as oil and gas, chemical, and petrochemical.
We have the ready inventory of Forged Full Coupling in the different size ranges of 7/16 Npt, 3/4 Npt, 9/16 Npt, 9/16-18 Emt,1 1/4 Emt, 1-1/2 Emt, 1 Inch, 2 Inch, 3 Inch, 4 Inch, 5 Inch, 5.3 Inch, 7.3 Inch, 8 Inch Socket Weld and Threaded Half Coupling.
Socket Weld Half Coupling Standard Specifications
Standards
ANSI / ASME B16.11, MSS SP-79, 83, 95, 97, BS 3799
Pressure Class
2000LBS, 3000LBS, 6000LBS, 9000LBS
Types
Socket Weld (Weld In)| Threaded / Screwed (NPT or BSPP)
Dimensions
ASME/ ANSI B16.11 | MSS-SP-79, 83, 95, 97 | BS3799 | BS4504 | BS10
Size Range (inches)
1/8″~4″ (DN6~DN100)
Forms
Half/Full/Reducing Coupling
Threaded Full Coupling in Stainless Steel 304/304L, SS 316/316L, 904L, Alloy 20, Carbon A234 WPB, Nickel 200, Monel, Inconel, Hastelloy C22, Duplex Steel 2205, Titanium, Copper Nickel, SMO 254, Aluminum, Brass, Cast Iron, Galvanized, MS Socket Weld Half Coupling. Get best Price List.
ASME B16.11 Forged Fittings Types
If you are looking for ASME B16.11 Fittings types, weight chart, size chart, tolerance, and dimensions with drawings then kindly click the below-mentioned forms of pipe fittings as per your requirements to get the complete details. For the quick quote / price list click here.
Threaded Full Coupling Material Grades
| Stainless Steel Forged Coupling: | ASTM A182/SA182 F304, F304L, F316, F316L, F304H, F316H, F317, F317L, F321, F321H, F347, F347H, F446, F904L |
|---|---|
| Carbon Steel Forged Coupling: | ASTM/ ASME A 105 F42, F46, F60, F65, F52, F56, and F70, ASTM/ ASME A 350 LF 2, A350 LF3 |
| Alloy Steel Forged Coupling: | ASTM / ASME A 182 GR F5, F 9, F 11, F 12, F 22, F 91 |
| Duplex & Super Duplex Forged Coupling: | ASTM A 182 –F51 / F52 / F53 / F54 / F55 / F57 / F59 / F60 / F61 S 31803, S 32205, S 32550, S 32750, S 32760 |
| Nickel Alloy Forged Coupling: | ASTM / ASME SB 151, 152, 61, and 62 UNS NO. C 70600 (CU -NI- 90/10) , C 71500 (CU -NI- 70/30) / Nickel Alloy Forged Fittings ASTM / ASME SB 564 / 160 / 163 / 472, UNS 2200 (NICKEL 200) , UNS 2201 (NICKEL 201), UNS 4400 (MONEL 400), UNS 8825 INCONEL (825) , UNS 6600 (INCONEL 600), UNS 6601 (INCONEL 601) , UNS 6625 (INCONEL 625) , UNS 10276 (HASTELLOY C 276), UNS 8020 (ALLOY 20 / 20 CB 3), |
| Brass Forged Coupling: | Brass CA 360, CA 345 and CA 377 / SAE J530, SAE J531 and ASA |
ASME B16.11 Coupling Dimensions
ASME B16.11 Full Coupling - Socket Weld - Dimensions

Dimensions of Socket Weld Full Coupling (NPS 1/2 to 4, Class 3000)
| NPS | Socket Bore | Depth Socket | Bore DIA | Socket wall THK | Laying lengths | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | J | D | C | Coupling E |
Half coupling F |
|||
| 1/2 | 21.95 21.70 |
10 | 16.6 15 |
4.65 4.10 |
9.5 | 22.5 | ||
| 3/4 | 27.30 27.05 |
13 | 21.7 20.2 |
4.90 4.25 |
9.5 | 23.5 | ||
| 1 | 34.05 33.80 |
13 | 27.4 25.9 |
5.70 5.00 |
13 | 29 | ||
| 1.1/4 | 42.80 42.55 |
13 | 35.8 34.3 |
6.05 5.30 |
13 | 30 | ||
| 1.1/2 | 48.90 48.65 |
13 | 41.7 40.1 |
6.35 5.55 |
13 | 32 | ||
| 2 | 61.35 61.10 |
16 | 53.5 51.7 |
6.95 6.05 |
19 | 41 | ||
| 2.1/2 | 74.20 73.80 |
16 | 64.2 61.2 |
8.75 7.65 |
19 | 42.5 | ||
| 3 | 90.15 89.80 |
16 | 79.5 46.4 |
9.50 8.30 |
19 | 44.5 | ||
| 4 | 115.80 115.45 |
19 | 103.8 100.7 |
10.70 9.35 |
19 | 47.5 | ||
Dimensions of Socket Weld Half Coupling (NPS 1/2 to 2, Class 6000)
| NPS | Socket Bore | Depth Socket | Bore DIA | Socket wall THK | Laying lengths | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | J | D | C | Coupling E |
Half coupling F |
|||
| 1/2 | 21.95 21.70 |
10 | 12.5 11 |
5.95 5.20 |
9.5 | 22.5 | ||
| 3/4 | 27.30 27.05 |
13 | 16.3 14.8 |
6.95 6.05 |
9.5 | 23.5 | ||
| 1 | 34.05 33.80 |
13 | 21.5 19.9 |
7.90 6.95 |
13 | 29 | ||
| 1.1/4 | 42.80 42.55 |
13 | 30.2 28.7 |
7.90 6.95 |
13 | 30 | ||
| 1.1/2 | 48.90 48.65 |
13 | 34.7 33.2 |
8.90 7.80 |
13 | 32 | ||
| 2 | 61.35 61.10 |
16 | 43.6 42.1 |
10.90 9.50 |
19 | 41 | ||
ASME B16.11 Full Coupling - Threaded - Dimensions
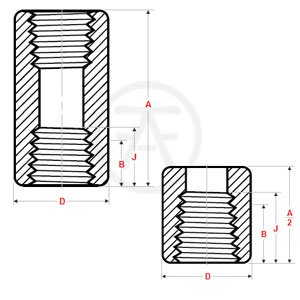
Dimensions of Threaded Full Coupling (NPS 1/2 to 4, Class 3000)
| NPS | Length | Outside Dia | Min Thread Length | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | D | B | J | |
| 1/2 | 48 | 28 | 10.9 | 13.6 |
| 3/4 | 51 | 35 | 12.7 | 13.9 |
| 1 | 60 | 44 | 14.7 | 17.3 |
| 1.1/4 | 67 | 57 | 17 | 18 |
| 1.1/2 | 79 | 64 | 17.8 | 18.4 |
| 2 | 86 | 76 | 19 | 19.2 |
| 2.1/2 | 92 | 92 | 23.6 | 28.9 |
| 3 | 108 | 108 | 25.9 | 30.5 |
| 4 | 121 | 140 | 27.7 | 33 |
Dimensions of Threaded Half Coupling (NPS 1/2 to 4, Class 6000)
| NPS | Length | Outside Dia | Min Thread Length | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | D | B | J | |
| 1/2 | 48 | 38 | 10.9 | 13.6 |
| 3/4 | 51 | 44 | 12.7 | 13.9 |
| 1 | 60 | 57 | 14.7 | 17.3 |
| 1.1/4 | 67 | 64 | 17 | 18 |
| 1.1/2 | 79 | 76 | 17.8 | 18.4 |
| 2 | 86 | 92 | 19 | 19.2 |
| 2.1/2 | 92 | 108 | 23.6 | 28.9 |
| 3 | 108 | 127 | 25.9 | 30.5 |
| 4 | 121 | 159 | 27.7 | 33 |
ASME B16.11 Socket Weld Full Coupling Tolerance
ASME B16.11 Socket Weld Coupling Dimenssional Tolerance

| "A" - Center to bottom of socket | FOR SIZES 1/8" AND 1/4" |
± 0.03" |
|---|---|---|
| 3/8", 1/2" AND 3/4" | ± 0.06" | |
| 1", 1-1/4", 1-1/2" AND 2" | ± 0.08" | |
| 2-1/2", 3", AND 4" | ± 0.10" | |
| "B" - Bore diameter of socket | FOR SIZES 1-1/2" AND SMALLER |
+ 0.020" - 0.000" |
| 2", 2-1/2", 3" AND 4" | + 0.025" - 0.000" |
|
| "C" - Socket wall thickness | MINIMUM = 1.09 T (BUT NOT LESS THAN 5/32") T = WALL THICKNESS OF NOMINAL PIPE |
|
| "D" - Bore diameter of fitting | FOR SIZES 2" AND SMALLER |
± 0.030" |
| 2-1/2", 3" AND 4" | ± 0.060" | |
| "E" - Bottom to bottom of sockets - couplings | FOR SIZES 1/8" AND 1/4" |
± 0.06" |
| 3/8", 1/2" AND 3/4" | ± 0.12" | |
| 1", 1-1/4", 1-1/2" AND 2" | ± 0.16" | |
| 2-1/2", 3", AND 4" | ± 0.20" | |
| "F" - Bottom of socket to opposite face - half couplings | FOR SIZES 1/8" AND 1/4" |
± 0.03" |
| 3/8", 1/2" AND 3/4" | ± 0.06" | |
| 1", 1-1/4", 1-1/2" AND 2" | ± 0.08" | |
| 2-1/2", 3", AND 4" | ± 0.10" | |
| "G" - Welding gap | APPROXIMATELY 0.06" RECOMMENDED GAP BEFORE WELDING |
|
| "H" - Minimum flat | MINIMUM FLAT = 0.75 X MINIMUM SOCKET WALL THICKNESS |
|
Q: What is a threaded coupling?
A: A threaded coupling refers to a type of fitting used to connect two pipes or tubes with threaded ends. It consists of two pieces with interlocking threads that can be screwed together, creating a secure and leak-proof connection.
Q: How does a threaded coupling work?
A: A threaded coupling works by utilizing the threads on the ends of pipes or tubes to create a tight and reliable joint. The two pieces of the coupling are screwed together, compressing the threads and creating a seal. This allows for easy assembly and disassembly of the connected pipes or tubes.
Q: What are the advantages of using threaded couplings?
A: Some advantages of using threaded couplings include:
- Ease of installation: Threaded connections are relatively simple to assemble, requiring no special tools or equipment.
- Versatility: Threaded couplings can be used in various applications and are compatible with a wide range of pipe or tube materials.
- Resilience: Threaded connections are typically strong and resistant to vibration, making them suitable for applications where stability is important.
- Reusability: Threaded couplings can be easily disassembled and reassembled multiple times, making them convenient for maintenance or modifications.
Q: Are there any limitations or considerations when using threaded couplings?
A: Yes, there are a few limitations and considerations to keep in mind:
- Leakage potential: While threaded couplings generally provide a secure connection, there is a possibility of leaks if the threads are damaged, worn out, or not properly aligned during assembly.
- Limitations on high-pressure systems: Threaded couplings may not be suitable for extremely high-pressure applications as the threads can potentially fail under excessive pressure.
- Thread compatibility: It is crucial to ensure that the threads of the coupling and the pipes or tubes are compatible to achieve a proper fit and prevent leakage.
Q: What is a forged coupling?
A: A forged coupling refers to a type of coupling made by forging, a manufacturing process that involves shaping metal using localized compressive forces. It is commonly used to connect two pipes or tubes in various industrial applications.
Q: What are the different types of forged couplings?
A: There are several types of forged couplings, including:
- Full Coupling: A full coupling is a forged coupling with both ends designed to connect pipes or tubes of the same diameter.
- Half Coupling: A half coupling is a forged coupling with one end designed to connect to a pipe or tube, while the other end is left unthreaded for welding onto another component.
- Reducing Coupling: A reducing coupling is a forged coupling that allows for the connection of pipes or tubes with different diameters.
- Swage Nipple: A swage nipple is a specialized type of forged coupling that is used for transitioning between different pipe sizes or types, typically with one end threaded and the other end unthreaded for welding.
Q: What are the advantages of using forged couplings?
A: Some advantages of using forged couplings include:
- Strength and durability: Forged couplings are known for their exceptional strength and durability, making them suitable for high-pressure and heavy-duty applications.
- Resistance to corrosion: Depending on the material used, forged couplings can exhibit excellent resistance to corrosion, ensuring a longer service life.
- Enhanced structural integrity: The forging process helps to improve the overall structural integrity of the coupling, resulting in a reliable and robust connection.
MSS SP-97 Threaded Half Coupling Applications
Oil and Gas
Nuclear Power & Defence
Petrochemical
LNG
Desalination
Mining & Minerals
Myanmar, Nepal, Thailand, Vietnam, Philippines, Malaysia, Indonesia,
Singapore, Taiwan, Tasmania, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Cambodia,
Australia, New Zealand, Afghanistan, Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan,
Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Iran, United Arab Emirates(UAE), Saudi Arabia,
Oman, Yemen, Iraq, Azerbaijan, Turkiye, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Kenya,
Egypt, South Sudan, Eritrea, Djibouti, Ethiopia, Libya, Rwanda, Mali,
Niger, Chad, Central Africa Republic, Nigeria, Cameroon, Somalia, DRC,
Uganda, Tanzania, Angola, Zambia, Madagascar, Malawi, Namibia, Benin,
Zimbabwe, Botswana, Lesotho, South Africa, Algeria, Tunisia, Morocco,
Eswatini, Liberia, Sierra Leone, The Gambia, Senegal, Mozambique, Togo,
Mauritania, Burkina Faso, Ghana, Equatorial Guinea, Jordan, Timor-Leste,
Palestine, Laos, Armenia, Georgia, Maldives, Cyprus, Kuwait, Qatar, Peru,
Bahrain, Brunei, Finland, France, Germany, Ireland, Iceland, UK, US,
Greece, Hungary, Italy, Norway, Poland, Slovakia, Sweden, Canada, Fiji,
Romania, Cuba, Panama, Brazil, Colombia, Chile, Argentina, Venezuela,
Naypyidaw, Kathmandu, Bangkok, Hanoi, Manila, Kuala Lumpur, Jakarta, Tunis,
Jurong East, Taipei City, Hobart, Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte, Dhaka, Thimphu,
Phnom Penh, Canberra, Wellington, Kabul, Dushanbe, Bishkek, Astana, Abuja,
Tashkent, Ashgabat, Tehran, Abu Dhabi, Riyadh, Muscat, Sana’a, Baghdad, Pretoria,
Baku, Ankara, Damascus, Beirut, Jerusalem, Nairobi, Cairo, Juba, Asmara, Rabat,
Djibouti city, Addis Ababa, Tripoli, Kigali, Bamako, Niamey, N’Djamena, Bangui,
Yaoundé, Mogadishu, Kinshasa, Kampala, Dodoma, Luanda, Lusaka, Antananarivo,
Lilongwe, Windhoek, Porto-Novo, Harare, Gaborone, Maseru, Cape Town, Bloemfontein,
Algiers, Mbabane, Lobamba, Monrovia, Freetown, Banjul, Dakar, Maputo, Lomé, Dili,
Nouakchott, Ouagadougou, Accra, Malabo, Amman, Vientiane, Yerevan, Tbilisi, Rome,
Malé, Nicosia, Kuwait City, Doha, Lima, Manama, Bandar Seri Begawan, Paris,
Helsinki, Berlin, Dublin, Reykjavík, London, Washington D.C., Athens, Budapest,
Oslo, Warsaw, Bratislava, Stockholm, Ottawa, Suva, Bucharest, Havana, Panama City,
Brasília, Bogotá, Santiago, Buenos Aires, Caracas, Mumabi, Chennai, Bengaluru,
Kolkata, Hyderabad, Pune, Ahmedabad, Jaipur, Surat, Visakhapatnam, Indore, New Delhi
Lucknow, Nagpur, Kochi, Kanpur, Guwahati, Coimbatore, Noida, Ghaziabad, Patna















